Adapter Pattern
Purpose
The purpose of the design pattern
To translate one interface for a class into a compatible interface. An adapter allows classes to work together that normally could not because of incompatible interfaces by providing its interface to clients while using the original interface.
Examples
Examples of how the design pattern can be used
- DB Client libraries adapter.
- Using multiple different web services and adapters normalise data so that the outcome is the same for all.
UML
UML design pattern diagram
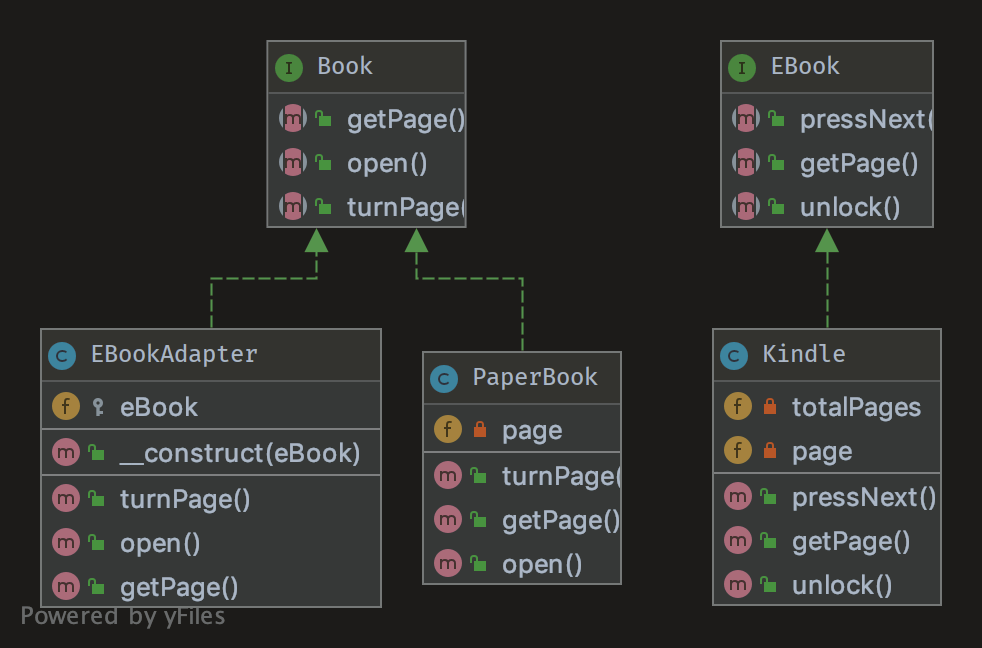
Code
Code snippets
Book
Book Interface
namespace DesignPatterns\Structural\Adapter;
interface Book
{
public function turnPage();
public function open();
public function getPage(): int;
}
EBook
EBook Interface
namespace DesignPatterns\Structural\Adapter;
interface EBook
{
public function unlock();
public function pressNext();
/**
* returns current page and total number of pages, like [10, 100] is page 10 of 100
*
* @return int[]
*/
public function getPage(): array;
}
EBookAdapter
The EBookAdapter class implements a foreign Interface (Book) but accepts the EBook Interface as a construct parameter and adapters the EBook methods to work with Book.
namespace DesignPatterns\Structural\Adapter;
/**
* This is the adapter here. Notice it implements Book,
* therefore you don't have to change the code of the client which is using a Book
*/
class EBookAdapter implements Book
{
public function __construct(protected EBook $eBook)
{
}
/**
* This class makes the proper translation from one interface to another.
*/
public function open()
{
$this->eBook->unlock();
}
public function turnPage()
{
$this->eBook->pressNext();
}
/**
* notice the adapted behavior here: EBook::getPage() will return two integers, but Book
* supports only a current page getter, so we adapt the behavior here
*/
public function getPage(): int
{
return $this->eBook->getPage()[0];
}
}
Kindle
A Kindle class (a type of EBook)
namespace DesignPatterns\Structural\Adapter;
/**
* this is the adapted class. In production code, this could be a class from another package, some vendor code.
* Notice that it uses another naming scheme and the implementation does something similar but in another way
*/
class Kindle implements EBook
{
private int $page = 1;
private int $totalPages = 100;
public function pressNext()
{
$this->page++;
}
public function unlock()
{
}
/**
* returns current page and total number of pages, like [10, 100] is page 10 of 100
*
* @return int[]
*/
public function getPage(): array
{
return [$this->page, $this->totalPages];
}
}
PaperBook
A PaperBook class (a type of Book)
namespace DesignPatterns\Structural\Adapter;
class PaperBook implements Book
{
private int $page;
public function open(): void
{
$this->page = 1;
}
public function turnPage(): void
{
$this->page++;
}
public function getPage(): int
{
return $this->page;
}
}
Tests
A PaperBook; utilising its methods and a Kindle which is passed through the EBookAdapter giving it the same methods as a Book (Not eBook).
public function testCanTurnPageOnBook()
{
$book = new PaperBook();
$book->open();
$book->turnPage();
$this->assertSame(2, $book->getPage());
}
public function testCanTurnPageOnKindleLikeInANormalBook()
{
$kindle = new Kindle();
$book = new EBookAdapter($kindle);
$book->open();
$book->turnPage();
$this->assertSame(2, $book->getPage());
}
Ready to bring your vision to life?
We believe in excellence, empathy, integrity, and transparency throughout the process. Our goal is to build fast, responsive websites that not only perform but also reflect your values and vision.